Professor Dr. Naci Görür: ‘Slipping 1 centimeter a year’

Prof. Dr. Naci Görür stated that Anatolia shifts westward by 1 centimeter per year and as a result, faults that accumulate stress cause serious earthquakes and said, “Elazığ has to be a city with an earthquake culture. Because a North Anatolian Fault (KAF) runs from Karlıova to Erzincan. This fault is the most dangerous fault in the world.”
Seismologist Roger Bilham, a lecturer at the University of Colorado Boulder, said that the energy discharge from the 6.8-magnitude earthquake in Elazığ 3 years ago had a positive effect on the magnitude of the Kahramanmaraş earthquakes on February 6. Stating that if the Elazığ earthquake had not happened, a major disaster could have been faced, Bilham said, “If the 2020 earthquake had not happened and the whole fault had broken in 2023, the magnitude of the earthquake could have reached 8.2 or even 8.4.”
‘Earthquake Resistant Cities Workshop’ was organized at Fırat University. Istanbul Technical University Geologist and Science Academy member Prof. Dr. Naci Görür, Colorado Boulder University lecturer seismologist Roger Bilham, Governor Ömer Toraman, AK Party MP Prof. Dr. Erol Keleş, Mayor Şahin Şerifoğulları, Fırat University Rector Prof. Dr. Fahrettin Göktaş, representatives of non-governmental organizations, faculty members and students attended the workshop where issues such as Turkey’s seismicity and the construction of earthquake-resistant cities were discussed.

PROF. DR. SEES: THE EAST ANATOLIAN FAULT LINE PRODUCES MANY SERIOUS EARTHQUAKES IN 500 YEARS
Speaking at the workshop, Prof. Dr. Naci Görür stated that Anatolia shifts westward by 1 centimeter per year and as a result, faults that accumulate stress cause serious earthquakes and said, “Elazığ has to be a city with an earthquake culture. Because a North Anatolian Fault (KAF) runs from Karlıova to Erzincan. This fault is the most dangerous fault in the world. There is also the Eastern Anatolia Fault (DAF), which runs from Karlıova to Malatya and Hatay. We have just had earthquakes and tens of thousands of people have died. There is also a fault going west of Malatya and from Pülümür to Ovacık. All of these faults are active. Do not think that an earthquake will happen every day. The Eastern Anatolia Fault line, which hits Bingöl, Elazığ and Malatya, produces many serious earthquakes in about 500 years. In other words, it moves 1 centimeter a year and no one can hear that centimeter shift. Anatolia moves 1 centimeter a year to the west, towards the Mediterranean. We cannot hear it, but these are accumulating stress there. That is to say, the accumulated stress of the earthquake that occurs in this neighborhood about once every 500 years is released for certain reasons. Pay attention, Elazığ is surrounded by active faults on all sides. The Southern Anatolian Fault, between Erzincan and Karlıova, accumulates stress every 250 years. I am especially telling the mayor, Elazığ is on a slice and the slice is surrounded by faults on all sides. After a certain period of time, Elazığ and its surroundings are completely surrounded by the faults I have drawn in red. These will produce earthquakes, and if they do, they will definitely affect Elazig at different scales.”

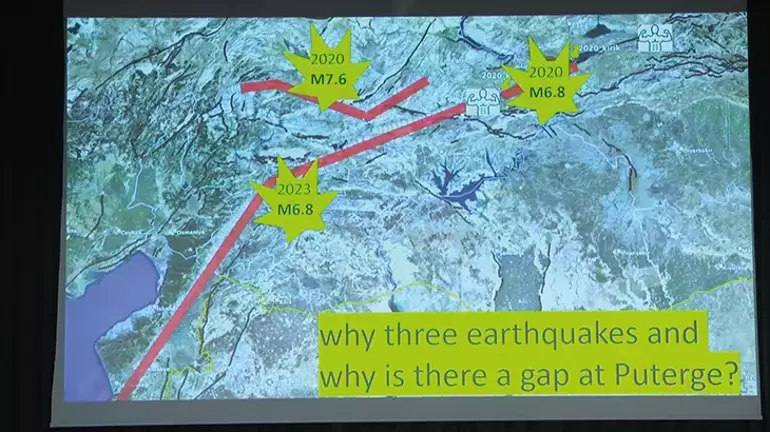
‘IF THE FAULT HAD BROKEN IN 2023, IT COULD HAVE REACHED 8.2 OR EVEN 8.4’
Seismologist Roger Bilham stated that if the 6.8 earthquake that occurred in Elazığ on January 24, 2020 did not occur, the Kahramanmaraş earthquakes on February 6 could reach up to 8.4 and said:
“The earthquake could have started from Bingöl at first and could have been a single earthquake, but it did not happen. If there had been a single earthquake, that is, if the 2020 earthquake had not happened and the whole fault had broken in 2023, the magnitude of the earthquake could have reached 8.2 or even 8.4. What stops these earthquakes is, firstly, the length of the fault, secondly, the side bends, obstacles and barriers on the fault, thirdly, the ‘crippling’ movement, which was first proven by Roger Bilham and other scientists on the Eastern Anatolian Fault, and another thing is the properties of the rocks at depth. In the field studies, we frequently saw the mineral ‘Serpentinite’ in places where sliding became difficult. Serpentinite has a soap-like structure and when you act on a very sudden movement, it prevents the movement as if there was a glue. In other words, serpentinite has a reducing effect on earthquake behavior. We took samples from here and sent them for analysis to the U.S. There is a basic rule, the behavior of rocks changes under temperature and pressure conditions. In our analysis here, if it is at 100 degrees Celsius, it makes it difficult to slide, just like serpentinite. However, if it is 3 kilometers or deeper, then it loses this effect and the slip progresses more easily. There is a gap between the southern end of the 2020 Sivrice earthquake and the northeast of the 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquake. These two fractures have not merged. This place is composed of ‘quartz schist’ rocks, like the sample we just mentioned and sent to the US. I am actually trying to tell you how such small minerals can stop big earthquakes.”